Simple purchasing processes are a matter of the past. Today, procurement departments operate in global structures throughout the company and beyond to identify a competitive supplier base. New products, unknown manufacturing processes, increasing production relocations require know-how in the production processes from the procurement teams.
More and more companies involve their suppliers and purchasing specifically in product development in order to build up knowledge and take the cost aspect into account in the early phase of product development. Transparent product costs including benchmarks are necessary to identify potential savings with the supplier and to determine target costs.
In our view, there are seven simple steps that procurement organizations can take to make their strategic procurement process (value sourcing) a success and increase their share of value creation.
Step 1: Accelerate supplier selection
How it starts: A request for a new component comes from product development. For purchasing organizations, the supplier selection process begins with various questions: Are there such products on the market? Which of my suppliers has designed similar products and could be considered for production? What were previous prices? How do I come to my calculation?
 The challenge is to find data that provides answers. This involves searching through in-house and sometimes outdated folder structures, filtering data, and exchanging information across departments. Database-driven searches with company-wide valid data saves time and resources and create a solid basis for the next step.
The challenge is to find data that provides answers. This involves searching through in-house and sometimes outdated folder structures, filtering data, and exchanging information across departments. Database-driven searches with company-wide valid data saves time and resources and create a solid basis for the next step.
Step 2: More reliability through valid data for cost calculations
Target costs can be established in two ways:
- Greenfield's approach by using valid benchmark values or
- Brownfield approach by using data collected from previous suppliers’ offers or from audits.
The data basis is crucial. It is important that underlying data are valid and withstand the comparison to the real supplier situation. It is simply a matter of being up to date, especially in areas that are subject to high fluctuations such as material prices, in some cases wages, and machine investments. Purchasing teams can ensure that changing framework conditions are considered in the accompanying review of target costs.
Step 3: Evaluate costs of manufacturing processes more easily with cost models
Companies looking for ways to optimize costs should focus on alternative manufacturing processes. For statements that are as reliable as possible, cost models are generally used that allow a realistic approximation of actual manufacturing times. They incorporate current developments in manufacturing technology and allow alternatives to be considered on a fact basis. Even in cases where the specific technology is not available in-house, there is no know-how and no empirical values. This allows the purchasing department to discuss and develop options together with the supplier that can lead to a significant optimization of costs and investments over the lifetime of a product.
Cost evaluation is optimized when there are more and more standards in cost accounting. Digitally available cost models, for example, support standardized costing in situations where complex manufacturing processes are to be evaluated company-wide by several procurement units.
Step 4: Establish comparability and standards for calculation methods
Setting up a planning or production process requires being able to compare various scenarios and suppliers under different premises. This must be done in a standardized manner so that factually correct conclusions can be drawn. With a costing methodology that is valid throughout the company, companies ensure that every costing is carried out in the same way for every scenario, irrespective of the supplier, the estimator, the time, and the location. Without costing standards, it is almost impossible to achieve reliable results in cost comparisons. In such a case, opportunities are missed to identify and address real potential for cost reduction.
Step 5: Determine reliable values for target costing and calculate achievable target prices
Different approaches such as top-down target costing or bottom-up target costing can be used for target price calculation.
- Top-down target costing makes it possible to define ambitious, yet realistic, target figures at a very early stage of product development. These can subsequently be monitored throughout the different business divisions. Top-down targets ensure products are developed within a framework that is economically viable.
- Bottom-up target costing also establishes expected costs for assemblies and components since previously known parameters at an early stage of product development. This reveals a margin that can be exploited for the profitable production of a component.
Both approaches are gaining in importance for purchasing and cost engineering since they are responsible for between 60 and 85 percent of the value added of a product depending on the sector of industry. The earlier the procurement department is included in the process, the higher the probability that the mutually defined targets will be reached.
Step 6: Make progress and identify cost reduction measures internally and with suppliers
Usually there will be discrepancies between the defined cost targets and the offers received from the supply chain. Such variances can be caused at all points in the supply chain, such as during in-house production or at the supplier's subcontractor.
During the product development process, these gaps can be addressed with suitable measures and ideally be closed. There may be a wide range of measures in both technical and commercial contexts that can be used to achieve the objectives.
 See our webinar video on how companies can overcome challenges in target costing: Meet Your Target Costs and Increase Your Margin with Effective Design-to-Cost.
See our webinar video on how companies can overcome challenges in target costing: Meet Your Target Costs and Increase Your Margin with Effective Design-to-Cost.
The structured and traceable approach to the collection, evaluation, implementation, and monitoring of cost reduction measures is a key feature for purchasing departments and the entire cost engineering team. Additional cost analyses and simulations with degrees of hardness can be carried out for the defined measures. They provide early indications of the area of possible cost optimization as well as the ability to achieve the cost targets.
Step 7: Increase efficiency with automated reports and workarounds
In cost engineering - the overall process of cost structure analysis - business units, various departments on the supplier side and other participants in the supply chain are equally involved. The groups must be informed in a timely and comprehensible manner about the respective status of costs and optimization plans.
Information paths can be implemented more efficiently through process automation. For example, calculations can be sent from the costing solution to other organizational units at the push of a button. Or variant management can be integrated to ensure that everyone involved, from the R&D department to the purchasing team, has a comprehensible view of cost developments.
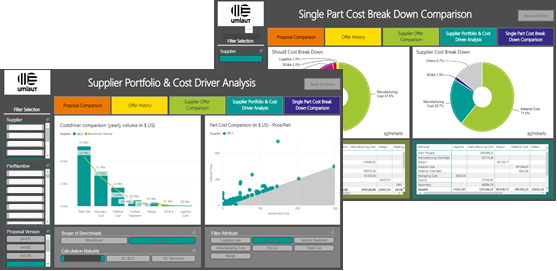
Source: Costing Reports umlaut (FACTON Partner)
Reporting mechanisms provide central information of a calculation and simplify responsive reporting. Interfaces to common reporting tools such as Tableau or Power BI also enable personalized dashboards and cross-functional reports. Transparency enables concerns to be addressed and resolved early in actions to be agreed upon.
With a global and collaborative strategy and the right software environment, the potential in Should Costing can be tapped across all stages of the value chain.
Read our white paper to learn in detail how EPC Should Costing can help you achieve better prices for purchased parts and increase the value-added share of procurement.